In the modern era of manufacturing which is very precise, non-destructive testing (NDT) is very useful in verifying quality without harming components. The use of imaging technologies, 2D industrial X-ray, and industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning, is widespread. Although both methods utilize X rays to detect objects, their data acquisition methods, resolution, and the applications of each differ considerably.
This guide provides a straightforward industrial X-ray vs CT scan comparison that is tailored for quality engineers, production teams, and other technical stakeholders.
Table of Contents
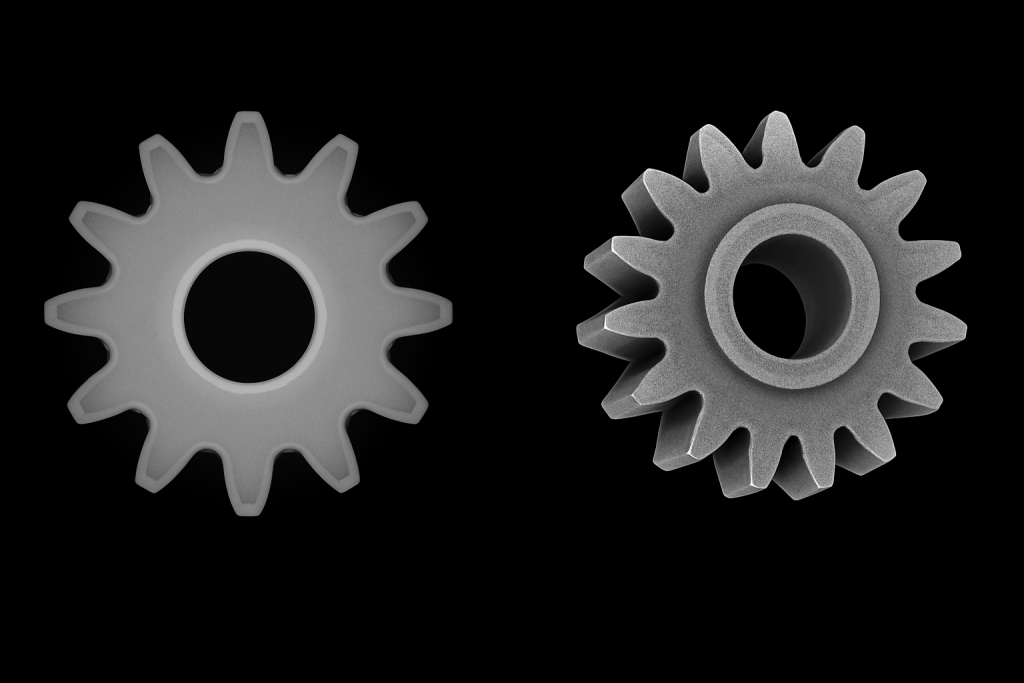
Comparison of industrial imaging methods: X-ray shows a 2D projection of the gear, while CT scan produces a detailed 3D reconstruction.
Core Imaging Principle: Projection vs. Tomographic Reconstruction
The main difference between these two imaging technologies lies in how they generate images.
- 2D Industrial X-ray technology capture single flat projection images, analogous to shadowgraph. While this method is useful for simpler components, it is rapid, and it suffers from the drawback of potentially masking essential internal details because of overlapping structures.
- Industrial CT Scanning involves rotating the object and capturing multiple X-ray images from various angles. These are then reconstructed into a 3D digital model made up of voxels, allowing for highly detailed internal inspection, dimensional analysis, and defect detection.
Analogy:
- X-ray = a photograph
- CT = a 3D digital twin generated from cross-sectional data
Technical Comparison: Imaging, Resolution, and Measurement
The differences between 2D X-ray and CT scanning extend to several technical parameters, which are summarized in the table below:
Parameter | 2D X-Ray | Industrial CT Scan |
Imaging Output | 2D grayscale image | 3D volumetric reconstruction |
Resolution | 0,1µm – 2000 µm | 0,5µm – 1000 µm (micro-CT and High Power LINAC -CT) |
Defect Visibility | Structural internal defects | Clear internal defect detection |
Dimensional Measurement | Only partially possible | High-accuracy internal measurement |
Material Penetration | Limited by density resolution and geometry | Limited by density resolution and geometry |
File Format | JPEG, TIFF | DICOM, Voxel, RAW, (STL) |
Scan Duration | Seconds | Seconds Minutes to any hours |
2D X-ray is ideal for high-speed inspection of parts where the detection of internal defects is paramount.
CT scanning enables micron-level internal inspection and precise measurements, which are particularly useful for complex geometries, castings and additively manufactured parts.
When to Use X-Ray vs. When to Use CT Scan
Deciding whether to use industrial X-ray or CT scanning largely depends on the complexity of the part, the inspection objectives, and operational constraints such as budget and throughput requirements.
Choosing between X-ray and CT depends on part complexity, inspection goals, and budget considerations.
Use 2D X-Ray if:
- You need fast pass/fail inspections with minimal setup and training.
- If the position of the internal faults is not decisive.
- Defects and part do not require volumetric measurement.
- You want a low-cost solution that fits into a high-throughput inspection workflow.
- Your inspection workflow requires minimal data processing, with visual checks being sufficient.
Use Industrial CT Scan if:
- If you need to determine the exact location of internal geometry and defects in your parts.
- Your goal is precise dimensional measurement, internal defect detection like porosity or cracks, or detailed reverse engineering.
- Your goal is precise dimensional measurement, internal defect detection like porosity or cracks, or detailed reverse engineering.
- You require integration with CAD software, finite element analysis (FEA), or digital twin workflows, enabling advanced simulation and predictive maintenance.
- Because of the depth of insight, defect detectability, and decreased destructive testing, you can invest in more expensive equipment and training up front.
- You gain access to sophisticated data output formats (RAW, DICOM, and STL) that facilitate automated AI defect detection and quantitative analysis.
- X-ray: Quickly spot surface flaws in welds or circuit boards, ideal when you need results without delay.
- CT: Aluminum die-cast porosity or verify the exact dimensions of molded parts with the detail only computed tomography can provide.
Conclusion
2D industrial X-ray and industrial CT scanning each have their roles in non-destructive testing, and together they provide a comprehensive toolkit. 2D X-ray is used in situations where speed and budget matter, delivering quick detection at hidden features. When the goal is internal examination, exact dimensional accuracy, and the creation of complete 3D digital representations for engineering processes, industrial CT scanning truly excels.
A strategic approach to imaging technology selection, grounded in rigorous evaluation of inspection objectives defined by these principles, can drive improvements to quality control, cost, and time-to-market for new products.
Xray-Lab provides advanced CT scanning services alongside high-speed industrial X-ray scanning for non-destructive quality inspection for years. From swift 2D scans to intricate 3D analyses, our imaging services enable smarter decisions at every step. We aid manufacturers in optimizing global workflows for speed, precision, and cost. Visit our webpage or reach out to us to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Does 2D X-Ray Excel Above the Others in High Volume Production Inspections?
Fast and simple to set up, 2D X-ray is perfect for finding common internal flaws in simpler parts. It is particularly helpful in high-throughput settings that require fast pass/fail outcomes without requiring intricate data processing.
What Makes Industrial CT Scanning Ideal for Reverse Engineering?
CT scanning is ideal for reverse engineering because it produces intricate 3D models of internal and external geometries. For precise simulation or redesign, engineers can transform scan data into CAD-compatible formats like STL.
Can Industrial CT Be Used for Both Defect Detection and Dimensional Analysis?
Indeed, industrial CT scanning allows for accurate dimensional measurements and the simultaneous detection of internal defects (such as cracks or porosity) from a single scan. Multiple tools or destructive testing are less necessary thanks to this dual capability.

